Epoxy is one of the most versatile materials you can keep in your woodworking toolkit. Whether you’re repairing, protecting, or creating a showpiece, there’s an epoxy product designed for the job. But not all epoxies are the same—some are made for bonding, others for finishing, and some for filling gaps. Let’s break down the main types of epoxy and where they shine in woodworking.
- Epoxy Adhesives – For Strong, Lasting Bonds
Epoxy adhesives are designed to bond wood and other materials with incredible strength. They’re typically a two-part system (resin and hardener) that cures into a rock-solid joint. Unlike traditional wood glue, epoxy can fill small gaps, making it perfect for irregular surfaces.
Best Uses:
• Repairing broken furniture joints (like chair rungs or table legs)
• Laminating wood veneers or bonding wood to metal, stone, or glass
• Outdoor or structural repairs where durability matters
- Epoxy Coatings – Protection and Beauty
Epoxy coatings are thinner formulas meant for spreading, brushing, or pouring over wood surfaces. Once cured, they create a hard, glossy, waterproof finish that enhances the natural beauty of the wood while protecting it.
Best Uses:
• Table and bar tops with a “glass-like” shine
• Live-edge river tables
• Sealing surfaces against moisture (especially in kitchens and bathrooms)
• Outdoor projects where weather resistance is essential
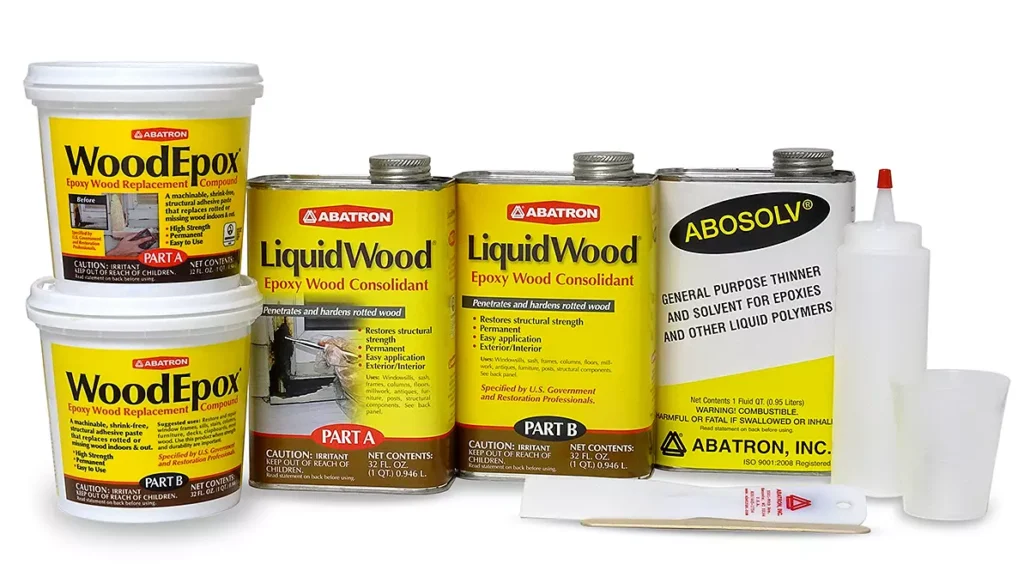
- Epoxy Fillers and Putties – Repairing Imperfections
Thicker epoxy formulations act as fillers or putties. These can be packed into cracks, knots, and voids in wood, then sanded, shaped, and finished once hardened. They’re often tinted with dyes or mixed with sawdust to better match the surrounding wood.
Best Uses:
• Repairing cracks, checks, and voids in slabs or boards
• Filling knot holes before finishing
• Rebuilding missing edges or trim details
• Decorative inlays with colored epoxy
- Marine Epoxy – The Waterproof Workhorse
Marine epoxy is specially formulated to resist water, humidity, and rot. It penetrates deeply into the wood fibers, sealing them against moisture damage. If you’re building or repairing something that will live outdoors, marine epoxy is your best friend.
Best Uses:
• Boat building and repairs
• Outdoor furniture and garden structures
• Protecting wood in damp or humid environments
- Casting & Deep-Pour Epoxy – For Creative Projects
Casting epoxy (sometimes called deep-pour epoxy) is designed to cure slowly without overheating, allowing you to pour thicker layers at once. This makes it ideal for artistic projects where you want to fill large voids or encapsulate objects.
Best Uses:
• River tables and live-edge designs
• Casting decorative pieces or encasing objects in resin
• Filling large voids or defects in wood slabs
Final Thoughts
Epoxy isn’t a one-size-fits-all material. The type you choose depends on the project at hand:
• Adhesive epoxy for strong bonding
• Coating epoxy for protective finishes
• Filler epoxy for repairs
• Marine epoxy for waterproofing
• Casting epoxy for deep pours and artistic designs
Once you understand the different types, epoxy becomes a powerful ally in your woodworking shop—capable of saving a repair, elevating a design, or protecting your work for years to come.